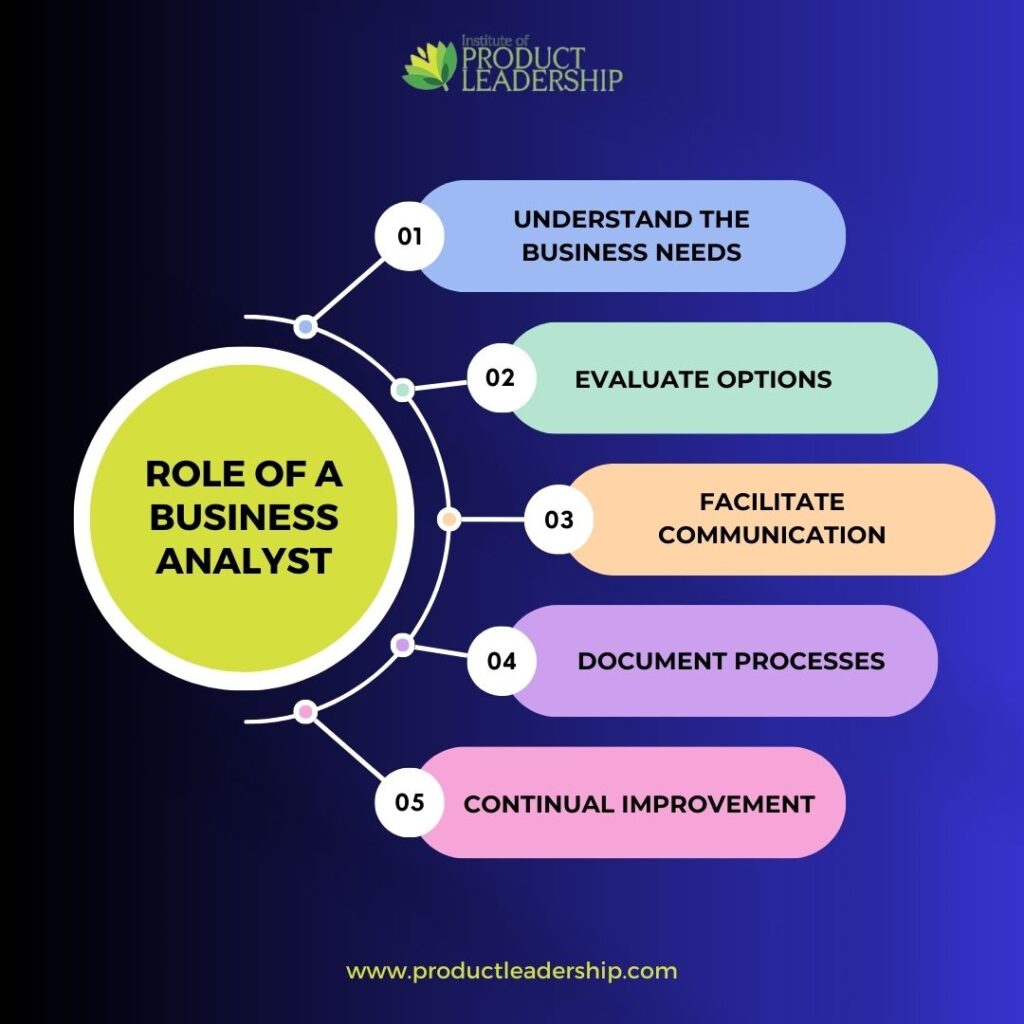
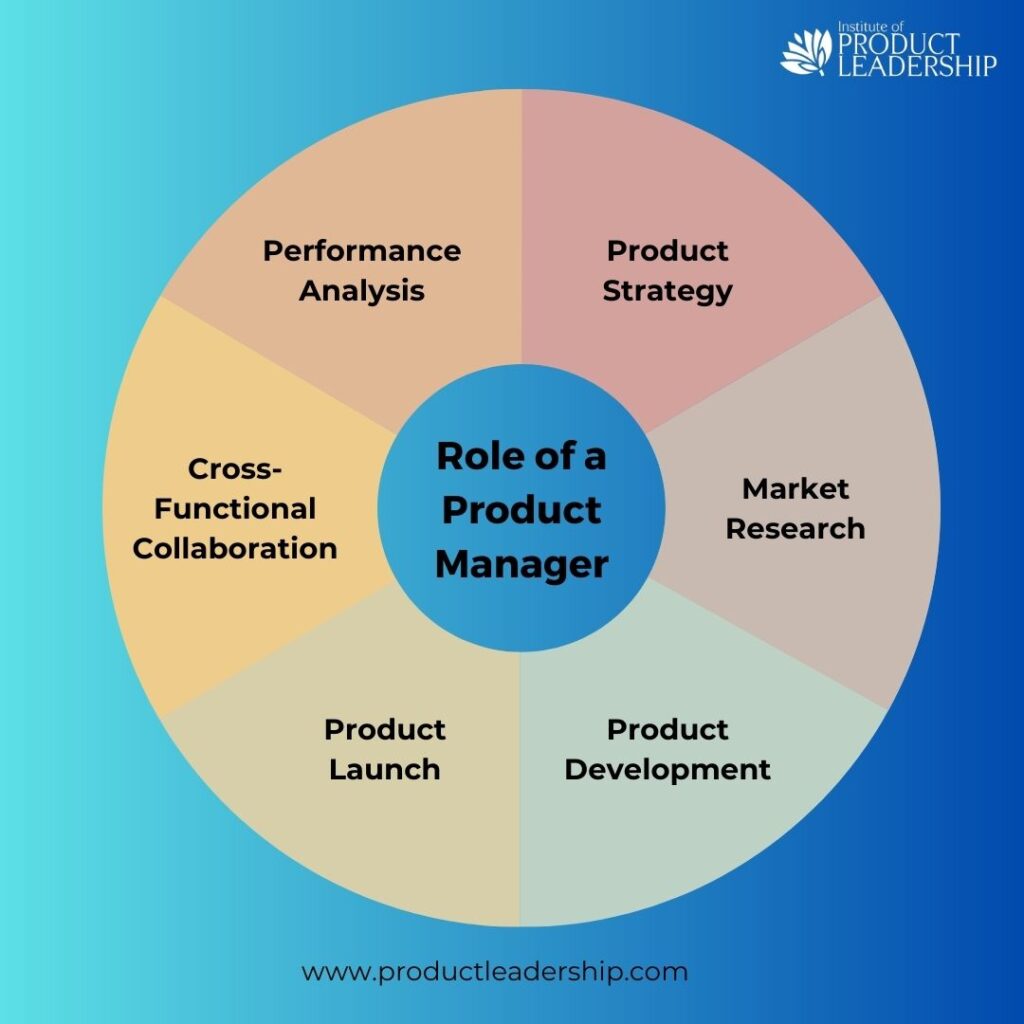
1. Product Strategy: The primary role of Product Manager develops a comprehensive product strategy by understanding market trends, customer needs, and business objectives. They define a clear vision and roadmap for the product, considering factors such as target market, competitive landscape, and potential growth opportunities.
2. Market Research: Extensive market research is conducted to gather insights on customer preferences, pain points, and emerging trends. This research helps identify market opportunities, competitive threats, and areas for differentiation, enabling the Product Manager to make informed decisions throughout the product lifecycle.
3. Product Development: The Product Manager plans and executes successful product launches, considering factors such as target audience, competitive positioning, pricing, and go-to-market strategies. They collaborate with marketing, sales, and other teams to create awareness, generate demand, and drive customer adoption.
4. Product Launch: The Product Manager plans and executes successful product launches, considering factors such as target audience, competitive positioning, pricing, and go-to-market strategies. They collaborate with marketing, sales, and other teams to create awareness, generate demand, and drive customer adoption.
5. Cross-Functional Collaboration: The Product Manager collaborates effectively with various teams, such as engineering, design, marketing, sales, and customer support. They align efforts, facilitate communication, and ensure cross-functional coordination to achieve product goals deliver a seamless customer experience, and drive business success.
6. Performance Analysis: The Product Manager continuously monitors and analyzes key product metrics, customer feedback, and market trends. They use data-driven insights to evaluate product performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize the product’s success. This analysis helps in identifying opportunities for feature enhancements, addressing user pain points, and staying ahead of the competition.