5 Easy Steps of Product Positioning Process
- product management
- 5 min read
By Manila Rauniyar – Senior Director Product Marketing at Clear
Effective product positioning is fundamental to the success of any marketing strategy, especially when introducing a new product to the market. Positioning involves carving out a distinct space in the minds of potential customers, ensuring that your product stands out among competitors. This article delves into the essentials of product positioning, providing key takeaways and actionable steps to create a powerful and unique market presence.
Key Takeaways:
- Product positioning is the strategic exercise of determining the position of a product or service in the market.
- It involves identifying the unique features of your product and effectively communicating its value to potential customers.
- Key steps in product positioning include knowing your target audience, understanding product features, creating unique selling propositions, assessing competitors, promoting product benefits, and maintaining brand positioning.
- Product positioning should focus on creating a distinct image and identity for the product or brand in the minds of end users.
- Effective product positioning requires understanding the diversity of the target segment, avoiding pitfalls in the search for unique selling propositions, serving both current and future customer needs, finding the right balance in messaging, and breaking biases within the organization.
What is Product Positioning?
Product positioning is a strategic exercise that we employ to determine the position of a product or service within the market. It entails identifying the unique features of your product compared to others in the market, enabling you to concentrate on effective messaging and clearly communicate its value to potential customers.
Steps in Product Positioning
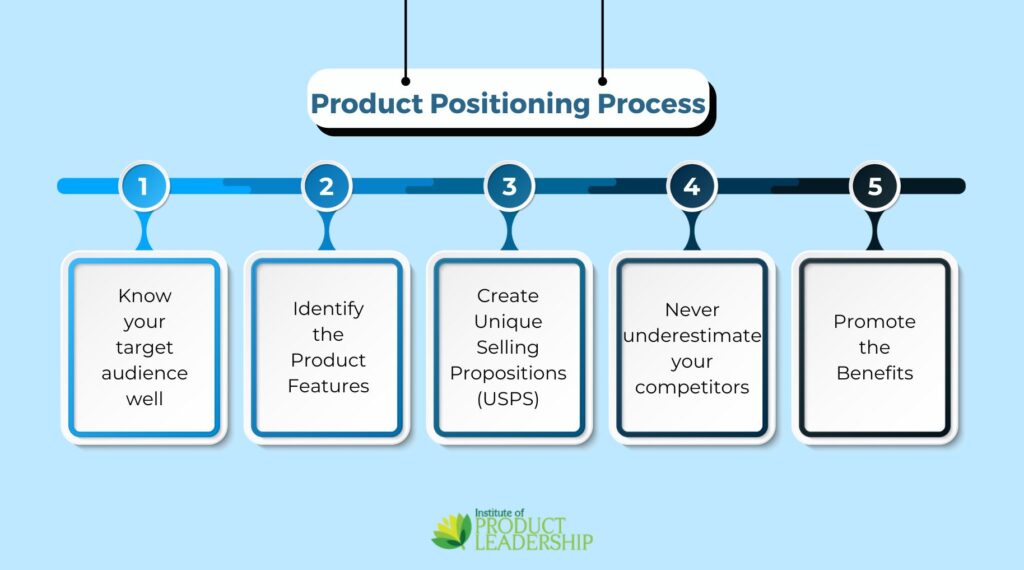
Here are simple steps to help you streamline the product positioning for your company/product:
1. Know your target audience well: You should know about your audience, but if you don’t know what they need to hear, you would be squandering your time and would be barking up the wrong tree with your right message. Knowing your target audience involves knowing the specific needs of the audience as well.
2. Identify the product features: It is very important for the marketers that they themselves are aware of the features and benefits of the products. It is well said that you really can’t sell something unless and until you yourself are convinced of it. A marketer selling a smart phone should himself also use the same smart phone handset for the customers to believe him.
3. Unique selling Propositions: Every product should have USPs; at least some features which are unique and different from those previously launched products in the market. The organizations must create USPs of their brands and effectively communicate the same to the target audience.
4. Never make a mistake of underestimating your competitor: A marketer must be knowledge about his competitor’s offerings. You need to convince the consumer how your product is better than the competitors. The marketers must always strive hard to have an edge over their competitors. A good example of this type of product positioning is the comparison pages found on many SaaS websites
5. Promote the benefits: A marketer must be knowledge about his competitor’s offerings. You need to convince the consumer how your product is better than the competitors. The marketers must always strive hard to have an edge over their competitors.
5 To Do's of Product Positioning
Product positioning is creating a distinct image and identity for a product or brand in the minds of end users.
1. Positioning by Cohort: Understand the diversity of the segment your targeting and build a list of Cohort identifiers.
2. Avoid the two pit falls when in search of USP: To do this you have to search just the new features list for USP’s and do not miss to look outside the core competency.
3. Don’t just limit with serving the pain: Value proposition is a promise a product or an offering makes to its end customer. Typically, an equation of not just helping meet the current need but also make the customer future ready.
4. Getting the right balance-messaging: A product positioning message is a promise from the provider to the customer/consumer. So your messaging has to be honest, not to overboard that it does resonate with the customer and not to ordinary that it doesn’t stick or create a lasting impact.
5. Breaking the Bias: As a Product Manager, you should be able to break a bias that comes from your product owner, Strategic teams, developers, and the company itself in terms of chalking out what the product can do right now and giving insights back to them about what further enhancements would be required in the product to have a stronger product positioning.
Summary
Effective product positioning is a nuanced and strategic process that requires a deep understanding of your target audience, product features, and competitive landscape. By following these steps and focusing on creating a distinct and compelling image for your product, you can ensure that it stands out in the market and resonates with customers. Remember, successful product positioning not only addresses current customer needs but also prepares them for future challenges, thereby establishing a lasting connection and fostering brand loyalty.
About the Author
Manila Rauniyar – Senior Director Product Marketing at Clear
Frequently Asked Questions
The product positioning process is a strategic approach used by businesses to define how they want their products to be perceived by their target audience in comparison to competitors.
Product positioning is crucial as it helps businesses stand out in the market, attract the right customers, and create a distinct identity for their products or services.
The process typically involves steps such as market research, target audience analysis, competitive analysis, unique value proposition (UVP) development, and positioning statement creation.
The four types of product positioning are
- Value Positioning
- Attribute Positioning
- Price Positioning
- Competitor Positioning
Product positioning refers to how a product is perceived by consumers in relation to other products in the market. Its role is to create a distinct image and identity for the product in the minds of the target audience. Effective product positioning helps a company differentiate its offerings, communicate unique benefits, and attract the right customers.
Product positioning strategy is the plan or approach a company uses to establish a specific position for its product in the market. It involves identifying the unique selling points (USPs) of the product, understanding the target audience's needs and preferences, and then crafting marketing messages and tactics to convey the product's value proposition effectively.
Product positioning is crucial because it directly impacts a product's success in the market. It helps a company stand out in a crowded marketplace, resonates with the right audience, and fosters brand loyalty. Effective positioning can lead to increased sales, market share, and long-term profitability.
Product positioning is the process of defining how a product occupies a distinct place in consumers' minds. There are several types of product positioning:
- Attribute-based positioning: Emphasizing specific product features or attributes.
- Benefit-based positioning: Focusing on the benefits or advantages of using the product.
- Price-based positioning: Positioning the product based on its price relative to competitors.
- User-based positioning: Positioning the product for a specific user group or persona.
- Competitor-based positioning: Positioning the product by comparing it to competitors.
The basic concept of product positioning is to shape how consumers perceive a product by highlighting its unique qualities and advantages. It involves creating a mental image of the product in the target audience's minds that aligns with the company's marketing objectives.
Product positioning can take various forms based on different strategies:
Positioning by Cohort: Tailor your product positioning to specific customer segments or cohorts with distinct needs and characteristics.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Position your product based on its unique features or benefits that differentiate it from competitors.
Value Proposition: Create a positioning strategy that not only addresses immediate customer needs but also prepares them for the future.
Balanced Messaging: Craft honest and impactful messaging that resonates with customers without exaggeration or understatement.
Breaking Bias: Overcome internal biases and align product positioning with customer feedback and evolving market demands.
These different types of product positioning strategies allow companies to adapt their approach to suit their unique products and market conditions.
Market research helps businesses understand customer needs, preferences, and market trends, providing valuable insights for crafting a strong positioning strategy.
Target audience analysis helps identify the ideal customers and tailor positioning to meet their specific needs and expectations.
Product positioning focuses on the product's place in the market, while branding encompasses the overall perception and reputation of the company and its products.
Common mistakes include overlooking competitor analysis, neglecting to refine the positioning over time, and failing to align the product with its positioning.
A USP highlights the unique benefits of a product, making it more appealing to consumers and reinforcing its position in the market.
Effective strategies include communicating the positioning clearly in marketing materials, staying consistent, and monitoring market changes.
Success can be measured through key performance indicators (KPIs) such as increased market share, customer satisfaction, and revenue growth, indicating the effectiveness of the positioning strategy.